Foot amputation refers to the surgical removal of part or all of the foot due to conditions such as diabetes-related infections, poor blood circulation, or serious injury. Depending on how much of the foot is affected, doctors may perform different types of amputations, like Transmetatarsal, Lisfranc, Chopart, or Symes. Each type has unique recovery needs. With the right prosthetic support, physical therapy, and emotional care, many individuals can regain balance, walk confidently, and return to daily activities.
Foot Loss Recovery: Overcoming Physical & Emotional Challenges
Anyone undergoing a foot loss also faces physical and emotional trauma. Yes, it is only human to experience loss of balance, confidence, and frustration for getting help from others for simple tasks. At times, the mental trauma may lead to depression and relationship issues.
The road to recovery and rehabilitation is challenging but not impossible. However, with the latest prosthetic solutions, timely intervention, proper diagnosis, correct surgery, and support, it is possible to regain normalcy. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore foot amputation, types, causes, and how prosthetic solutions can help individuals regain mobility.
What Is Foot Amputation?
When a part or the whole foot is removed through surgery, it is called foot amputation, which is necessary because of severe trauma, infection, vascular disease, or diabetes complications.
Understanding the Two Main Categories of Foot Amputations
- Partial Foot Amputation: It is the removal of the foot partially, preserving the remaining structures.
- Complete Foot Amputation: When the whole foot is surgically removed, including a portion of the ankle joint.
Common Causes of Foot Amputations
There are several critical reasons why foot amputations are performed, including saving a limb or a life. Common causes include:
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic individuals may develop severe wounds caused by poor blood flow and nerve damage, which often leads to infections and the need for amputation.
- Serious Injuries
When individuals suffer crush injuries, severe accidents, or burns, it may impact foot tissue, leading to amputation.
- Deep Infections
An individual may develop infections in bones (osteomyelitis) or deep tissues, which may lead to amputation.
- Cancer or Tumours
Cancerous tumours inside the foot need surgical removal.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Development of gangrene or tissue death also requires amputation.
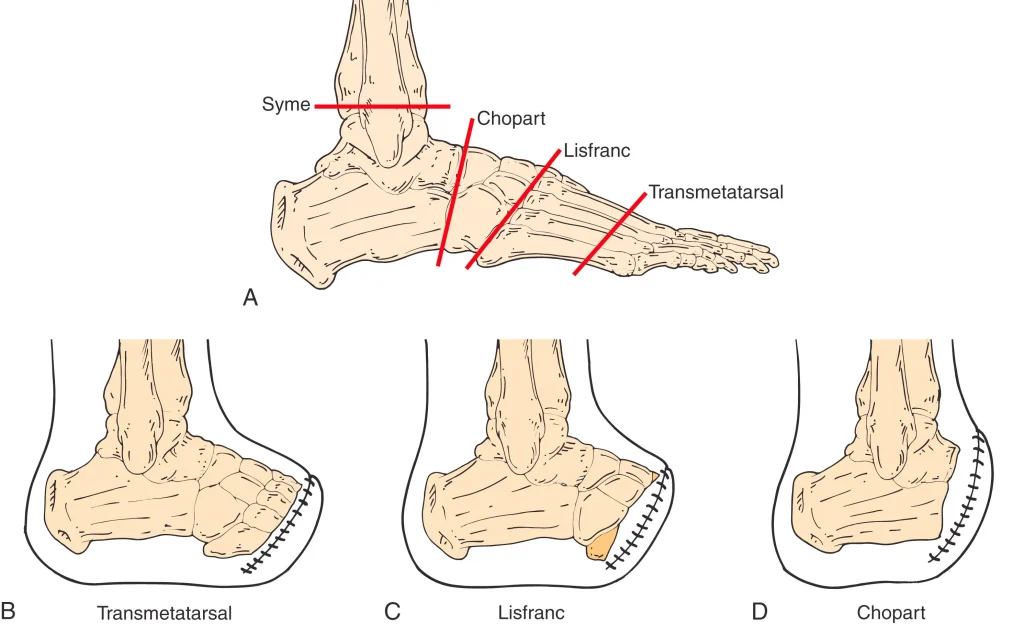
What are the 4 Types of Foot Amputations?
The level and type of foot amputation have a significant impact on mobility, prosthetic fitting, and rehabilitation. Common types:
1. Transmetatarsal Amputation (TMA): Forefoot Loss & Recovery
A Transmetatarsal Amputation (TMA) is the surgery of the front part of the foot to remove it. This partial foot amputation is for:
- Diabetic foot ulcers, which affect the toes or forefoot.
- Localised gangrene or severe infection.
- Irreparable trauma to the front of the foot.
A TMA allows for the fitting of a specialised partial foot prosthesis, designed to restore balance and foot contour. For more in-depth information, explore our detailed guide on Transmetatarsal Amputation.
2. Lisfranc Amputation: Midfoot Preservation for Balance
A Lisfranc amputation removes the forefoot at the first, second and third cuneiform bones or tarsometatarsal joints, keeping the midfoot and heel intact. Lisfranc partial foot amputation is suitable for patients who still have good heel pad integrity and no skin issues, as it provides a stable platform for prosthetic solutions. It’s often performed for:
- Untreated infections or ulcers.
- Lisfranc joint complex injuries.
This type of amputation enables a well-fitting partial foot prosthesis that supports balance and function. To learn more, read about Lisfranc Amputation: What to Expect.
3. Chopart Amputation: Addressing Midfoot Challenges
A Chopart amputation is the removal of the midfoot through surgery while saving the heel and ankle. This extensive partial foot amputation has unique challenges, as the key tendons are lost. Consequently, individuals need Ankle-Foot Orthosis (AFO) support or custom-made prosthetics to prevent potential foot drop and have proper gait. his amputation is for:
- Midfoot infections or gangrene.
- Severe midfoot trauma.
Understanding the specific needs after this procedure is crucial for effective rehabilitation. Discover more about Chopart Amputation: Challenges & Solutions.
4. Syme’s Amputation: Ankle-Level Preservation for Mobility
This type of amputation is the removal of the whole foot at the ankle joint, but preserving the heel pad. This unique preservation enables patients to bear weight on the residual limb, allowing them to walk with assistance in some cases. It is an option in the following cases:
- Lower-level amputations are insufficient.
- The entire foot is severely compromised by trauma or infection.
- A below-knee amputation can be avoided.
The Symes amputation typically allows for excellent mobility with a well-fitted ankle-foot prosthesis. For further details, see Symes Amputation: Life After Surgery.
Need Guidance on the Right Prosthesis After Foot Amputation?
Get personalised support and expert prosthetic solutions tailored to your amputation level.
👉 Book a free consultation with KARE Prosthetics & Orthotics today.
Recovery After Foot Amputation

The journey after foot amputation extends beyond the operating room.
1. Emotional Healing
Limb loss is severely traumatic and leads to emotional challenges. The individual undergoes decreased self-esteem, mental health issues, and the frustration of being dependent. Although it is natural to experience grief, anger, fear, or frustration after an amputation, you are not alone. Therefore, do not hesitate to seek recovery support.
2. Choosing the Right Prosthetic or Orthotic Solution
Different solutions are available depending on the specific foot amputation:
- Partial Foot Prosthesis: This is a customisable prosthesis that matches the specific contour and fills the void of the residual foot. Ultimately, providing balance and functionality.
- Ankle-Foot Prosthesis: Suitable for amputations such as Symes, it provides comprehensive support and gait assistance.
- Custom Orthotic Inserts: Suitable for individuals with TMA or Lisfranc amputations. It optimises even pressure distribution and support.
Amputees must go through proper rehabilitation and prosthetic planning for effective and smoother your recovery.
3. Nursing and Medical Care
Complete recovery is possible with proper post-operative care. For instance, an intensive nursing diagnosis for a post-surgical wound includes :
- Risk for infection
- Impaired tissue integrity
- Impaired mobility
- Disturbed body image
Your dedicated care team will typically comprise a skilled surgeon, an experienced prosthetist, a physical therapist, and often a counsellor to address the holistic needs of your recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetic Foot Amputation
You can protect your feet from Diabetic foot amputation by taking daily foot care, wearing proper footwear, and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Also, you must inspect your feet from time to time, wash and dry them properly. Consult a doctor for ulcers, corns, or calluses.
Doctors decide to amputate a foot when the foot is damaged or deteriorating due to severe trauma, poor blood flow, infections, tumours, or wounds. Amputation is the final solution when the foot cannot be salvaged and becomes a threat to the individual.
If you refuse to amputate in life-threatening conditions such as sepsis or gangrene, it can lead to serious complications. You may suffer due to the spreading infection, or it may lead to death. However, doctors usually agree with the patient. The medical team then offers palliative care, pain management, and care till the patient’s death.
It takes 4 to 6 weeks to recover from a toe amputation. The wound heals over time and pain reduces within a week, but phantom pain can be felt for a year. People can return to everyday life within a few weeks.
Yes, you can walk and lead an everyday life with proper care, support, and a suitable prosthetic foot that enables walking, working, and an active lifestyle. Physical therapy will help you build strength and balance, allowing you to move confidently with your prosthetic limb
Feeling some pain after surgery initially is normal. The pain is manageable with prescribed medication. Sometimes, amputees feel “phantom pain” in the amputated foot, but this feeling goes away after treatment.
The cost of an artificial foot varies depends on the provider, features, complexities, and type of material used. It may cost between ₹30,000 and ₹1.5 lakh.
KARE Prosthetics & Orthotics India: Your Recovery Partner
At KARE Prosthetic and Orthotics India, we have been working with individuals recovering from partial foot amputations, particularly in diabetes-related cases. We primarily focus on:
- Custom Prosthetic Fitting: Customising prosthetic devices so they can offer comfort, function, and a natural gait.
- Gait Training: We guide you through physiotherapy and exercises to relearn balance and walk effectively.
- Pain Management: We apply various pain management strategies to alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.
- Counselling for families and caregivers: We provide guidance, offer support, and train caregivers.
“My mother walked again within 6 weeks of her Symes amputation, thanks to the team at KARE. They didn’t just treat her, they empowered her.” As the daughter of a patient from Bangalore
Final Thoughts
Amputation of the foot is not a full stop; it opens new possibilities. Individuals can get back their mobility and become self-dependent with prosthetic technology and solutions. The KARE Prosthetics & Orthotics team is committed to supporting you with custom-designed prosthetic solutions, expert guidance, and assistance, and helping boost your confidence and mobility.
Are you ready to take the next step to regain mobility? Book a consultation with us.