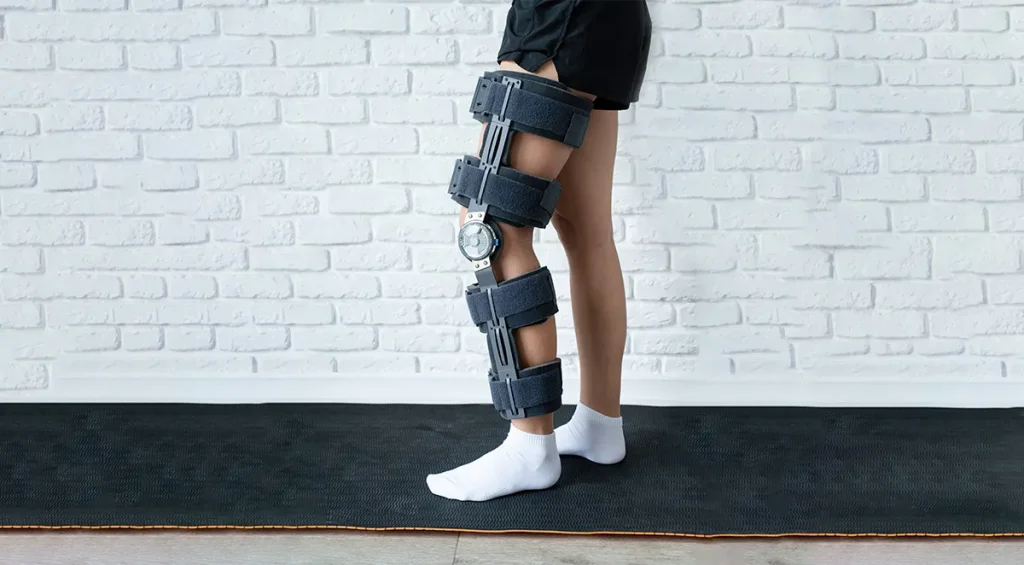
Children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) face progressive muscle weakness affecting their ability to walk and move. However, there is hope, as a Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis (KAFO) can significantly extend mobility. Thus, the individual has greater chances of improving their quality of life.
In this blog, we’ll discuss how KAFOs help children with DMD, explore the parts of the Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis, and compare different Ankle Foot Orthosis types.
What Is a Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis (KAFO)?
A Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis is a tailored orthosis that can be used to support the leg from the thigh to the foot. KAFOs, therefore, play an essential role in stabilising weak muscles, improving walking posture, and delaying the need for a wheelchair.
Benefits of KAFOs include:
- Boost stability: KAFOs do not allow the knees to buckle and prevent unsafe movements.
- Better posture: KAFOs encourage proper body alignment.
- Increased mobility: Children can walk for longer periods
- Less fatigue: KAFOs reduce tiredness from walking.
- Prevents Contracture: Maintains joint flexibility and prevents stiffness.
The timely use of KAFOs in the initial development period can significantly improve long-term walking ability in children with DMD. So, let us first understand DMD.
What Is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)?
DMD is a progressive and degenerative muscle disorder. This disorder is due to mutations in the dystrophin gene, which produces dystrophin protein. Therefore, the lack of dystrophin weakens the muscles over time.
DMD primarily affects boys, with symptoms appearing between ages 2 and 5:
- The child frequently falls, has difficulty running and jumping
- Faces trouble standing up from the floor
- The child has enlarged calf muscles due to abnormal muscle tissue
- Walking on the toes has a waddling
The child experiences progressive difficulty walking and requiring Knee-Ankle-Foot Orthoses (KAFOs). With time, the child has to use a wheelchair. DMD may affect the heart and respiratory muscles.
How Can KAFOs Help Children With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
DMD primarily targets the hip muscles, the thighs, and the calves. With the progression of DMD, standing and walking become difficult. Without support, many children transition to full-time wheelchair use by their early teens.
Here’s how KAFOs make a difference:
- Supports weak muscles and offers strength.
- KAFOs keep the knees stable and prevent risk of falls.
- Allows children to independently participate in activities.
- Walking more helps delay the transition to a wheelchair.
- Improves self-esteem and mental well-being.
Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis Parts
It is essential to know the parts of a Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis as it helps caregivers and users understand its function and the maintenance needs associated with it.
| Part | Function |
| Thigh Section | Wraps around the upper leg for alignment and support. |
| Knee Joint | A hinge that allows controlled knee bending and extension. |
| Calf Section | Provides lower leg stability. |
| Ankle Joint | Ankle movement is stable and supports balance. |
| Footplate | It can fit inside the shoe to maintain proper foot positioning. |
| Straps & Fasteners | Help to secure the KAFO. |
What Is an Ankle Foot Orthosis (AFO)?
An Ankle Foot Orthosis (AFO) is custom-fitted orthopedic device to support the ankle and foot. The lightweight AFOs help to improve walking ability, stability, and alignment for individuals who have weakening muscles, nerve disorders, or other mobility challenges.
AFOs are used for:
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)
- Stroke-related foot drop
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Early-stage Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
- Spinal cord injuries or nerve damage
How Does an AFO Work?
AFOs hold the ankle and foot in the proper position. This prevents unsafe movements, inward or outward rolling of the ankle. Consequently, it reduces tripping, improves gait, and decreases tiredness while walking.
Benefits of an AFO:
- Makes the ankle and foot stable for safer walking
- Aligns correct posture and overall balance
- Prevents falls and injuries
- Prevents deformities caused by muscle imbalance
- Enhances confidence and independence
Types of AFOs
Selection of AFO depends on the needs and activity level of the user:
- Solid AFO: Offers rigid support for maximum stability
- Hinged AFO: Enables controlled ankle movement for a more natural gait
- Dynamic AFO: Made for active users, offering flexibility and support
- Posterior Leaf Spring AFO: Helps in foot lifting to prevent tripping (ideal for foot drop)
AFOs are best used in the early stages of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy or other mobility conditions. It helps in delaying future complications and promote independence.
What Is a Hip Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis (HKAFO)?
A Hip Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis (HKAFO) is a orthopedic device used to support the leg, including the hip, knee, ankle, and foot. It is custom -made for users suffering from lower limb weakness or paralysis. HKAFO provide stability for standing and walking.
HKAFOs are typically used for conditions such as:
- Advanced Stages of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
- Severe Spinal cord injuries
- Spina bifida
- Advanced cerebral palsy
- Progressive neuromuscular disorders
How Does an HKAFO Work?
HKAFO offer full-leg alignment and joint stabilisation. They prevent unsafe movements and allow the user to stand and walk with walkers or crutches.HKAFOs also distributes body weight evenly, reduce strain on weak muscles and joints.
Benefits of an HKAFO:
- Offers complete support for standing and walking
- Reduces falls and joint deformities
- Enables upright posture and weight-bearing
- Boosts independence and improved daily function
- Helps maintain muscle and bone health through supported movement
KAFO vs. AFO: Which Orthosis Is Right for DMD?
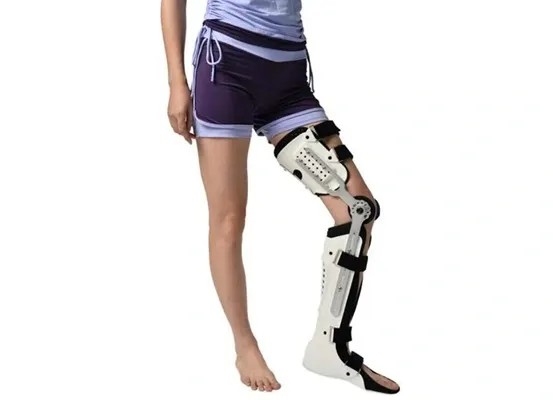
In the early stages of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, a lower-level orthosis, like an Ankle Foot Orthosis (AFO) may be enough. As muscle weakness progresses, a KAFO provides additional support.
| Orthosis Type | Description | Best For |
| Solid AFO | Rigid support that prevents unwanted ankle movement. | Early-stage DMD with mild ankle instability. |
| Hinged AFO | Allows limited, controlled ankle motion for a more natural walking pattern. | Children who need moderate flexibility. |
| Dynamic AFO | Provides flexibility for active children while still offering necessary support. | Active children with mild to moderate weakness. |
| Posterior Leaf Spring AFO | Helps lift the foot while walking to reduce tripping and improve gait. | Children experiencing foot drop or tripping. |
| AFO (General) | Supports only the ankle and foot. | Mild muscle weakness, early-stage DMD. |
| KAFO (General) | Complete support for the knee, ankle, and foot. | Advanced muscle weakness, difficulty standing or walking. |
When Should a KAFO Be Introduced?
Early intervention is crucial for the care of DMD. Consider introducing a KAFO when you notice:
- The child falls frequently or trips while walking
- Knee buckling or collapsing
- When the child has difficulty standing from a seated position
- More fatigue after short periods of walking
- Declining walking ability
The timely use of KAFOs can slow disease progression, allowing children to remain active and mobile for longer.
Comparison of AFO, KAFO, and HKAFO for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Choosing the right orthotic device depends on the severity of muscle weakness, stage of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), and the child’s mobility needs.
| Feature | AFO (Ankle Foot Orthosis) | KAFO (Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis) | HKAFO (Hip Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis) |
| Support Level | Ankle & Foot only | Knee, Ankle & Foot | Hip, Knee, Ankle & Foot (full-leg support) |
| Primary Purpose | Stabilises the ankle and foot, prevents foot drop or tripping | Provides knee stability and proper lower-leg alignment | Offers maximum stability for standing and walking |
| Best For | Mild muscle weakness or early mobility issues | Moderate to advanced muscle weakness affecting knee control | Severe weakness or paralysis of the entire leg |
| Common Conditions | – Early-stage DMD- Stroke recovery- Mild cerebral palsy- Foot drop | – Advanced DMD- Post-polio syndrome- Moderate cerebral palsy- Lower-limb spinal injuries | – Advanced DMD- Spina bifida- Severe cerebral palsy- Spinal cord injuries |
| Mobility Goals | Improve walking pattern & prevent tripping | Maintain independence and delay wheelchair use | Enable standing & walking using walkers or crutches |
| Weight-Bearing Ability | Partial support | Moderate to full support for legs | Full support for entire lower body |
| When Typically Introduced | Early in the condition’s progression | When knees need extra support due to muscle decline | In advanced stages where hip stability is needed |
| Examples of Use | Walking aid for mild weakness | Walking safely despite knee instability | Standing and walking with severe leg and hip weakness |
Why Choose KARE Prosthetics & Orthotics for KAFOs
At KARE Prosthetics & Orthotics, we offer custom orthotic solutions for children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Our experts provide personalised care, blending advanced technology with compassion.
What sets us apart:
- KAFOs tailored to each child’s needs
- Pediatric-friendly designs for comfort and usability
- Follow-up and adjustment services
- Collaboration with doctors and therapists
Visit KARE Prosthetics & Orthotics to explore customised KAFO solutions today.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main purpose of a KAFO?
A KAFO supports weak muscles in the leg, improves stability, and allows children with DMD to walk independently for a longer time.
2. What are the main parts of a knee, ankle foot orthosis?
The primary parts include the thigh section, knee joint, calf section, ankle joint, footplate, and adjustable straps.
3. Which is better for DMD, KAFO or AFO?
An AFO is suitable for early-stage DMD with mild weakness, while a KAFO is better for advanced stages where both knee and ankle support are required.
4. How long does a child need to wear a KAFO each day?
Wearing schedules vary based on the child’s condition, but typically 4–6 hours a day, gradually increasing under the guidance of an orthotist.
5. Can KAFOs prevent the need for a wheelchair?
While they can’t prevent eventual wheelchair use, KAFOs significantly delay the transition, keeping children mobile and independent longer.
Conclusion
A Knee Ankle Foot Orthosis (KAFO) is a transformative tool for children living with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). KAFOs are essential for lower-limb support, prolonged walking ability, and enhancing balance and posture.
At KARE Prosthetics & Orthotics, we have custom, clinically-appropriate KAFOs tailored to your child’s unique needs, and we’re committed to helping children walk longer, safer, and with confidence.
To learn more about assistive devices, book a consultation with our team today.